Third Term Basic Science Lesson Note for JSS2
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
Week 1 & 2
Topic: Thermal Energy
Introduction
Energy transfer is the process of transmitting or transferring energy from one place to another. The word thermal means heat. Thermal energy is the transfer of heat from one place to another.
Heat Flow
Energy transfer means that energy moves from one place to another (without changing form). The process of heat flow from the sun to us is referred to as radiation. The process of heat flow from the soup to the spoon discussed is referred to as conduction. There is the third process of heat flow known as convection. Therefore, heat flow means that heat energy is transferred from a hotter part of an object to the cooler part of the object. Heat is a form of energy that flows from a hot area to a cold one. When you are in the hot sun, you feel hot. The heat travels from the sun through the atmosphere to your skin. When you put a kettle of cold water on fire, the water gets hot. The heats flows or travels from the fire through the kettle into the water.
Transfer of Heat Energy
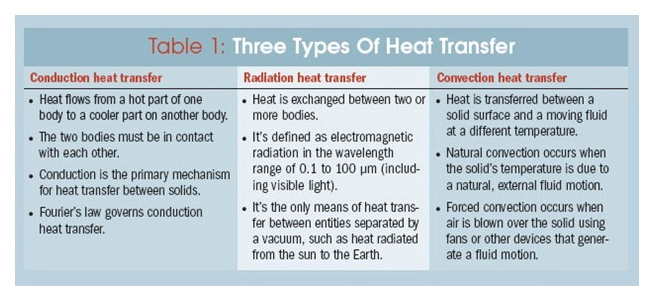
The three processes of heat transfer are conduction, convection and radiation.
Conduction
When particles in a matter (or substance preferably a metallic substance) are heated, the particles vibrate, hitting the successive ones (which are not in contact with the source of heat). This raises their temperature until all the particles in the metallic substances are heated up. In this way, heat is being conducted along the metallic substance and this process is called conduction.
Usually, heat flows from a hot to a cold body. You know that heat is a form of energy and a hot body has energy stored up (in form of potential energy) in it. In order to convert this potential energy into kinetic energy, heat then passes to another particle which has lower energy. Therefore, a hot body must lose heat energy to a cooler one.
There are good conductors and bad conductors of heat.
Good conductors of heat are substance s, which conduct heat readily; all metals are good conductors of heat.
Bad conductors are substances that do not conduct heat readily. Liquids and gases are bad conductors of heat. Water is an example of a bad conductor of heat. But mercury is a metallic liquid, hence it conduct heat readily.
Convection
Heat transfer in convection is peculiar with liquids. The heat flows from the bottom of a liquid container to the top by the actual movement of the liquid molecules. This transfer of heat by the movement of liquid molecules is known as convection
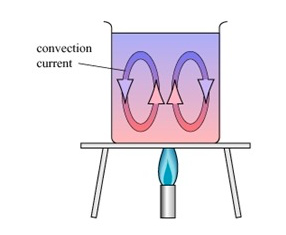
Radiation
Radiation is a method of heat transfer that does not require material medium for transmission. Heat energy is transmitted by means of waves. Heat energy from the sun reaches us by radiation. Heat can travel in invisible waves from hot places to cooler places. Heat travelling this way does not need any medium (solids, liquids or gases) to travel through. Heat can travel through a vacuum. A vacuum is a space in which there is nothing at all, not even air. There is a vacuum in space between the earth and the sun. The heat from the su travels through this vacuum to the earth and through the earth to other obects.

ASSESSMENT
- Define Radiation?
- The three processes of heat transfer are___
- What is energy transfer?
Week 3
Topic: Reproductive Health
Meaning of Reproductive Health
Reproductive health is the ability of people to have a satisfying and safe sex life and the capability to reproduce as well as the freedom to decide if, when and how often to do so.
Significance of Reproductive Health
Reproductive health is significant because it promotes good sexual health which enhances life and personal relations. It is also a prerequisite for social, economic and human development i.e. human energy and creativity is the driving force of development and this cannot be generated by a sick person. It sets the stage for health beyond the reproductive years for both men and women. Similarly, the health of a newborn is largely a function of the mother’s health, and nutritional status and her access to good health care. Furthermore, reproductive health takes care of reproductive health problems at various stages in life, thereby preventing health problems at later stages in life. It contributes enormously to physical and psychosocial comfort and closeness. Reproductive health creates awareness on the dangers associated with disease, abuse, exploitation, unwanted pregnancy, etc.
Care and Protection of the Reproductive System
This is done through:
- Circumcision of the male at childbirth reducing the effect of micro-organisms on the fore skin of the penis.
- Regular bathing of the individual and drying of the reproductive organs.
- Shaving of the pubic hair to avoid the growth of bacteria and fungi.
- Ensuring thorough cleanliness of the toilet system to avoid contracting diseases, such as candidacies.
- Washing of undies (pants) regularly.
- Using sanitary pads by females during menstruation to avoid getting stained and infections.
- Using tissue paper to clean up after urinating.
Breast Feeding
Breastfeeding is the normal way of providing young infants with the nutrients they need for healthy growth and development. Virtually all mothers can breastfeed, provided they have accurate information, and the support of their family, the health care system and society at large.
Colostrum, the yellowish, sticky breast milk produced at the end of pregnancy, is recommended by WHO as the perfect food for the newborn, and feeding should be initiated within the first hour after birth.
Exclusive breastfeeding is recommended up to 6 months of age, with continued breastfeeding along with appropriate complementary foods up to two years of age or beyond.
Importance of breastfeeding
Breastfeeding a baby exclusively for the first 6 months, and then continued breastfeeding in addition to appropriate solid foods until 12 months and beyond, has health benefits for both the mother and child.
Importance of breastfeeding for mother
Research shows that breastfeeding has significant health benefits for mothers.
Breastfeeding:
- Assists the uterus return to its pre-pregnant state faster.
- Can help women to lose weight after baby’s birth.
- Reduces the risk of ovarian cancer and pre-menopausal breast cancer.
- Reduces the risk of osteoporosis
- Reduces the risk of mothers with gestational diabetes developing Type 2 diabetes.
Importance of breastfeeding for baby
- Less illness
- Babies who are fed breast milk have a lower risk of :
- Gastro-intestinal (gut) illness
- Allergies
- Asthma
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Some childhood cancers
- Respiratory tract (chest) infections
- Urinary tract infections
- SIDS (cot death).
- Breastfed babies are less likely to be hospitalized.
Importance of Knowledge of Genetic Disorder in Family
A genetic disorder is a disease that is caused by an abnormality in an individual’s DNA. In other word, genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes. Abnormalities can range from a small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of an entire chromosome or set of chromosomes. Sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, cancer, obesity, mental illness, Alzheimer disease and Tay-Sachs disease are examples of genetic disorders
Knowledge of genetic disorder may assist the family by:
- Identifying the likelihood that certain diseases or conditions may develop based on genetic information, and then anticipating the timing of the expected disorder in the person’s life cycle.
- Helping families prepare pragmatically and emotionally for expected challenges, such as: living with uncertainty, care giving strains, and losses associated with various genetic conditions as they may unfold.
- Helping families create meaning that sustains hope and promotes mastery.
- Identify effective treatments, or teaching coping skills for disorders with little hope for treatment.
- Can lead to better care and management of the patient and ultimately to improved quality of life
ASSESSMENT
- Define reproductive health?
- List FIVE ways the care and protection of the productive system is done?
- Mention FIVE ways the Knowledge of genetic disorder may assist the family?
Week 4
Topic: Measurement
Introduction
Measurement is one of the fundamental concepts in experimental sciences, including physics. Measurement is the process of attaching a numeric value to an aspect of a natural phenomenon, such as the volume of the milk produced by a cow, in order to be able to describe that phenomenon accurately and make comparisons to other similar phenomena.
Importance of measurement
Unless we are able to measure some phenomena, we cannot say we scientifically know anything about that thing.
Measurement gives a base to understand the universe. All around us we are surrounded by various things. We might not note it but unconsciously we are actually “measuring” things and understanding them one way or the other. We are surrounded by Measurement.
Fundamental or Basic Unit
You measure things by defining a standard unit and then stating the measurement in terms of multiples of that unit. A fundamental unit of measurement is a defined unit that cannot be described as a function of other units.
The International System of Units (SI) defined seven basic units of measure from which all other SI units are derived.
SI Base Units
The SI unit system consists of seven base units, with a number of other units derived from those foundations. Below are the base SI units, along with their precise definitions:
- Meter (m) – The base unit of length
- Kilogram (kg) – The base unit of mass
- Second (s) – The base unit of time
- Ampere (A) – The base unit of electrical current
- Kelvin(degrees K) – The base unit of thermodynamic temperature
- Mole (mol) – The base unit of substance; the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilograms of carbon 12. When the mole is used, the elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles.
- Candela (cd) – The base unit of luminous intensity
These SI base units or commonly called metric units in summary are:
|
Measure |
Unit |
Symbol |
Area of Science |
|
Time |
Second |
s |
All |
|
Length or distance |
Meter or Metre |
m |
All |
|
Mass |
Kilogram |
kg |
Physics |
|
Electric Current |
Ampere |
A |
Physics |
|
Temperature |
Kelvin |
K |
Physics |
|
Luminous Intensity |
Candela |
cd |
Optics |
|
Amount of Substance |
Mole |
mol |
Chemistry |
Although these SI base quantities are supposed to be a set of mutually independent dimensions, some may well be interdependent.
Derived Units
With these base units, we can combine them to form derived units, such as the Newton, acceleration or speed; as an example, let us look at speed. Speed is described by the following equation:

MEASURING DEVICES
Instruments for determining various quantities such as temperature, mass, height, length, voltage and mechanical force.
Temperature: physical quantity corresponding to the level of heat or cold, which is measured by means of a thermometer.
TO GET YOUR COMPLETE LESSON NOTE AT AN AFFORDABLE PRICE, HIT THE WHATSAPP BUTTON BELOW
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS