Third Term Basic Science Lesson Note for JSS1
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
SUBJECT:
BASIC SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY {BST} – BASIC SCIENCE
CLASS:
JUIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL 1
TERM:
THIRD
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1. Revision of last term work; Human reproduction (I) – Menstruation, ovulation, fertilization
2. Human reproduction (II) – Pregnancy (conception) – signs and symptoms of pregnancy; stages of growth of the fetus
3. Force – meaning and types, contact and non-contact force, magnetic and gravitational force
4. Calculation of gravitational force; Balanced and unbalanced forces; Friction – meaning, uses, advantages and disadvantages
5. Space travel – meaning, purpose, benefits and dangers of space travel
Mid-term project
6. Gravitation and weightlessness – meaning and effect
7. Earth and space – solar system, rotation and revolution, eclipse and season
8. Earth and space – solar system, rotation and revolution, eclipse and season
9. Satellite – meaning and uses
10. Consequences and implications of teenage pregnancy – physical, social and emotional implication, Effects of drugs, self-medication and drug abuse during pregnancy, causes and consequences of birth defects
11. Revision
12. Examination
WEEK ONE
HUMAN REPRODUCTION (I)
v Menstruation
v Ovulation
v Fertilization
Menstruation
Menstruation is the monthly flow or discharge of blood from the vagina of a woman at child bearing age. It is also called period. The first occurrence of menstruation is called menarche.
The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age. The periods, however may occasionally start as young as eight years old and still be considered normal.
The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is on the average of 28days. Menstruation stops occurring at menopause, which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age.
This flow of blood usually lasts between 2 to 7 days but on the average it is 5days
During pregnancy and for some time after childbirth, menstruation does not occur; this state is known as amenorrhea.
Menstrual disorders and problems associated with menstruation
1. Heavy period: This is when there is an unusual and excessive flow of blood. It can also cause an extension of the bleeding to seven days.
2. The absence of menstrual periods: This condition involves an absence of menstruation for 3 months or longer in a sexually mature woman who is not pregnant or breastfeeding.
3. Pain and discomfort: Just before and/ or during menstruation there can be that is severe enough to interfere with normal daily activities. Such pain is usually experienced in the abdominal region and lower back as well as abdominal bloating, breast tenderness, headache, sleep problem and mood swings.
4. Bleeding between menstrual periods: (Such as abnormal uterine bleeding, spotting) can be the symptom of another medical condition, which can vary from minor to serious. Women who experience abnormal uterine bleeding should contact a health care provider.
MENSTRUAL HYGIENE
1. Choose your method of sanitation: It is essential to choose one that has the lowest absorbency rate for your flow. Frequent switching between brands can make you uncomfortable.
2. Change sanitary pad regularly: Menstrual blood, once it has left the body gets contaminated with the body’s innate organisms. Therefore, the standard time to change a sanitary pad is once every six hours.
3. Wash yourself regularly: When you menstruate the blood tends to enter tiny spaces like the skin between your labia or crust around the opening of the vagina and you should always wash this excess blood away. This practice also tends to beat bad odor from the vagina region.so, it is important to wash your vagina and labia well before you change into a new pad. If you cannot wash yourself before you change make sure you wipe off the areas by using toilet papers or tissues
4. Don’t use soap or vaginal hygiene product: The vagina has its own cleaning mechanism that works in a very fine balance of good and bad bacteria. Washing it with soap can kill the good bacteria making way for infections. So you can use soap on the external parts but do not use it inside your vagina or vulva.
5. Use the right washing techniques always: Wash or clean the area in a motion i.e. from the vagina to the anus and never wash in the opposite direction. Washing in the opposite direction can cause bacteria from the anus to enter into the vagina and urethral opening leading to infection.
6. Discard your used sanitary products properly: It is essential to discard your used napkins or sanitary pads properly because they are capable of spreading infections. Wrap it very well before discarding it. It is also important that you wash your hand very well after discarding your used napkins.
7. Beware of a pad rash: A pad rash is something that you might experience during the period of heavy flow.it usually occurs when the pad has been wet for a long time and rubs along the thighs causing it to chaff.to prevents this from occurring try to stay dry during your periods.
8. Use only one method of sanitation at a time: Some women who have heavy flow during their periods may use several pads at a time this practice is bad because the two pads absorbs the blood and you don’t see that they are completely used up, so you are unlikely to change at regular and healthy interval. This can lead to rashes and infections.
9. Have a bath regularly: Having a bath is the best thing you can do for your body during your periods. Bathing not only cleanses your body but also gives you a chance to clean your private part very well.it also helps to relieve menstrual cramps, backaches and makes you feel much better at the end of it.
10. Be ready or always prepared during your periods: When you have your periods, it is important to be ready by making arrangement for extra cleaning and sanitary materials. Make sure you store them properly so that they don’t get contaminated
Ovulation
Ovulation is the part of the female menstrual cycle whereby a mature ovarian follicle discharges an egg (also known as an ovum, oocyte or female gamete). It is during this process that the egg travels down the fallopian tube where it may be fertilized by a sperm. The process of ovulation usually occurs between the 10th and 19th day into the menstrual cycle and this is the time when humans are most fertile.
Ovulation typically stops at menopause.
Note: that once a female child starts menstruating, ovulation automatically begins which means such a female child can get pregnant if there is sexual intercourse.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF OVULATION
1. Change in cervical fluid or mucus: Cervical fluid or mucus that resembles” egg white “is the sign that you are near ovulation or you are ovulating. Ovulation takes place on the day a woman has the most amount of wet fluid or mucus.
2. Change in basal body temperature: An increase in basal body temperature is a sign that ovulation, the cervix will be soft, high, open and wet.
3. Breast tenderness and sensitivity: During ovulation the breast becomes tender and sensitive.
4. Increase libido or sexual urge: During ovulation there is an increase in sexual urge in women
5. Increase in the sense of vision, smell and taste: During ovulation there is an increase in the sense of vision, smell and taste
Fertilization
This is the fusion of the male gamete (i.e. the sperm) and the female gamete (.i.e. the ovum) to form a zygote. It occurs in the fallopian tube of the female. After fertilization the zygote grows and develops to form the young one. The process of fertilization always results to pregnancy
CLASSWORK 1
1. What is ovulation?
2. State 4 ovulation sign
3. Define menstruation?
ASSIGNMENT 1
SECTION A
1. An increase in basal body temperature is one of the signs and symptoms of (a) menopause (b) pregnancy (c) growth (d) puberty
2. The vagina should be washed always with soap in other to make it healthy (a) true (b) false (c) maybe (d) partly correct
3. The fusion of the male and female gamete to form a zygote is known as (a) conception (b) fertilization (c) menopause (d) menstruation
4. Another word for menstruation is (a) period (b) pregnancy (c) fertilization (d) gamete
5. Which of these statements is true of a female child who menstruates? (a) she can become pregnant (b) she will not be happy again (c) she is easily irritated with life (d) her level of assimilation decreases
SECTION B
1. What is fertilization?
2. Mention 4 signs to show that someone is pregnant
3. Mention 3 menstrual disorder
WEEK TWO
HUMAN REPRODUCTION (II)
v Pregnancy
v Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
v Stages of growth of the fetus
Pregnancy (conception)
Conception is also known as pregnancy.it is the period between fertilization and the birth of the young one .In human, the period of pregnancy is about 9 months.
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
1. Food aversions: If a woman is newly pregnant she may feel repelled by the smell of some food. She may also find that certain food she used to enjoy as suddenly completely repulsive to her.
2. Mood swings: It is common to have mood swings during pregnancy due to the changes in the hormone in the body every woman respond differently to these changes.
3. Abnormal bloating: Hormonal changes in early pregnancy may lead to the feeling of bloating that is similar to the feeling some women have just before their period
4. Frequent urination: Shortly after a woman becomes pregnant, hormonal changes makes a chain of events that raises the rate of blood flow through the kidneys this cause your bladder to fill more quickly so you need to pee more often
5. Fatigue: Pregnant women tend to always feel tired and exhausted during pregnancy and this leads to sleepiness and sluggishness
6. Sore breast: The breast becomes swollen and sensitive during pregnancy due to its rising levels of hormones in their body
7. Missed period: If a woman missed her period, it is an indication that she is pregnant. Although it is possible to still experience the monthly menstrual period even when a woman is pregnant
8. High basal body temperature: If you have been charting your basal body temperature and you see that your body temperature has stayed elevated for 18days in a roll it is an indication that you are probably pregnant.
CARE NEEDED DURING PREGNANCY
1. Get pregnancy test as soon as you miss your period
2. Talk with your partner and someone else you trust
3. Begin antenatal care check-ups with a medical doctor
4. Follow proper antenatal care instructions which include avoiding all drugs and medicine not prescribed by a medical doctor
5. Eat nourishing foods rich in protein, calcium folic acid, iodine and iron and drink plenty of water and fruit juices
6. Get adequate rest and relaxation
7. Do not smoke cigarettes or take alcohol
MYTHS AND FACTS ABOUT PREGNANCY
A myth refers to something that many people believe but that does not exist in the reality. It is false. On the other hand, a fact is something that is known to be true, especially that can be proved. There are myths and facts about pregnancy especially in the African traditional set up.
MYTHS ABOUT PREGNANCY
1. Only pregnancy can make a woman miss her monthly period
2. All pregnant women vomit
3. Pregnancy makes you unclean before God
4. All pregnant women have morning sickness
5. Pregnant women should not dye their hair
6. Pregnant women shouldn’t eat fish
7. I can’t get pregnant if I have my period
8. I can’t get pregnant the first time I have sex
9. If I wash out my vagina after sex I won’t get pregnant
10.Pregnant women should not take baths
FACTS ABOUT PREGNANCY
1. Pregnant women should not carry heavy objects
2. Some women may experience some bleeding and yet be pregnant
3. Pregnant women should not change cat litter
4. Pregnant women should not drink alcohol
5. You can be pregnant for over a year
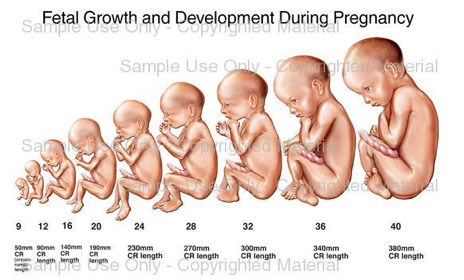
Stages of growth of the fetus
Each month a group of eggs (called oocytes) is recruited from the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Normally, one follicle in the group is selected to complete maturation. This dominant follicle suppresses all the other follicles in the group, which stop growing and degenerate.
The mature follicle opens and releases the egg from the ovary (ovulation). Ovulation generally occurs about two weeks before a woman’s next menstrual period begins. After ovulation, the ruptured follicle develops into a structure called the corpus lustrum, which secretes progesterone and estrogen. The progesterone helps prepare the endometrium (lining of the uterus) for the embryo to implant.
On average, fertilization occurs about two weeks after your last menstrual period. When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating around it to prevent other sperm from entering. At the moment of fertilization, a baby’s genetic make-up is complete, including its sex.
If a Y sperm fertilizes the egg, the baby will be a boy; if an X sperm fertilizes the egg, and the baby will be a girl.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone present in your blood from the time of conception. It is produced by cells that form the placenta and is the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. However, it usually takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins dividing rapidly into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days. The fertilized egg (called a blastocyst) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus where its next job is to attach to the endometrium (a process called implantation). Before this happens, the blastocyst breaks out of its protective covering. When the blastocyst establishes contact with the endometrium, an exchange of hormones helps the blastocyst attach. The endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix is sealed by a plug of mucus.
Within three weeks, the blastocyst cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo, and the baby’s first nerve cells have already formed. Your developing baby is called an embryo from the moment of conception to the eighth week of pregnancy. After the eighth week and until the moment of birth, the developing baby is called a fetus.
The development stages of pregnancy are called trimesters or three-month periods, because of the distinct changes that occur in each stage.
STAGES OF GROWTH: MONTH BY MONTH
Month 1
As the fertilized egg grows, a water-tight sac forms around it gradually; filling it with fluid. This is called the amniotic sac, and it helps cushion the growing embryo.
The placenta also develops. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers nutrients from the mother to the baby, and transfers wastes from the baby.
A primitive face will take form with large dark circles for eyes. The mouth, lower jaw, and throat are developing. Blood cells are taking shape, and circulation will begin. The tiny “heart” tube will be at 65 times a minute by the end of the fourth week. By the end of the first month, the baby is about 1/4 inch long – smaller than a grain of rice!
Month 2
The baby’s facial features continue to develop. Each ear begins as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds that eventually grow into arms and legs are forming. Fingers, toes and eyes are also forming. The neural tube (brain, spinal cord and other neural tissue of the central nervous system) is well formed. The digestive tract and sensory organs begin to develop. Bone starts to replace cartilage.
The head is large in proportion to the rest of the baby’s body. By the end of the second month, your baby is about 1 inch long and weighs about 1/30 of an ounce. At about 6 weeks, your baby’s heart beat can usually be detected. After the 8th week, your baby is called a fetus instead of an embryo.
Month 3
The baby’s arms, hands, fingers, feet, and toes are fully formed. The baby can open and close its fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails are beginning to develop and the external ears are formed. The beginnings of teeth are forming. The baby’s reproductive organs also develop, but the baby’s gender is difficult to distinguish on ultrasound.
By the end of the third month, your baby is fully formed. All the organs and extremities are present and will continue to mature in order to become functional. The circulatory and urinary systems are working and the liver produces bile. At the end of the third month, your baby is about 4 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce. Since the baby’s most critical development has taken place, the chance of miscarriage drops considerably after three months.
Month 4
The baby’s heartbeat may now be audible through an instrument called a Doppler. The fingers and toes are well-defined. Eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails, and hair are formed. Teeth and bones become denser. The baby can even suck his or her thumb, yawn, stretch, and make faces.
The nervous system is starting to function. The reproductive organs and genitalia are now fully developed, and the doctor can see on ultrasound if the baby is a boy or a girl. By the end of the fourth month, the baby is about 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces.
Month 5
One may begin to feel the baby move, since he or she is developing muscles and exercising them. This first movement is called quickening.
Hair begins to grow on the baby’s head. The baby’s shoulders, back, and temples are covered by a soft fine hair called lanugo. This hair protects the baby and is usually shed at the end of the baby’s first week of life. The baby’s skin is covered with a whitish coating called vernix caseosa. This “cheesy” substance is thought to protect baby’s skin from the long exposure to the amniotic fluid. This coating is shed just before birth. By the end of the fifth month, the baby is about 10 inches long and weighs from 1/2 to 1 pound.
Month 6
The baby’s skin is reddish in color, wrinkled, and veins are visible through the baby’s translucent skin. Baby’s finger and toe prints are visible. The eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
Baby responds to sounds by moving or increasing the pulse. One may notice jerking motions if baby hiccups. If born prematurely, the baby may survive after the 23rd week with intensive care. By the end of the sixth month, the baby is about 12 inches long and weighs about 2 pounds.
Month 7
The baby will continue to mature and develop reserves of body fat. The baby’s hearing is fully developed. He or she changes position frequently and responds to stimuli, including sound, pain, and light. The amniotic fluid begins to diminish.
At the end of the seventh month, the baby is about 14 inches long and weighs from 2 to 4 pounds. If born prematurely, the baby would be likely to survive after the seventh month.
Month 8
The baby will continue to mature and develop reserves of body fat. One may notice that the baby is kicking more. Baby’s brain is developing rapidly at this time, and the baby can see and hear.
Most internal systems are well developed, but the lungs may still be immature. The baby is about 18 inches long and weighs as much as 5 pounds.
Month 9
The baby continues to grow and mature: the lungs are nearly fully developed. The baby’s reflexes are coordinated so he or she can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light, and touch. Baby is definitely ready to enter the world!
One may notice that the baby moves less due to tight space. The baby’s position changes to prepare itself for labor and delivery. The baby drops down in the pelvis. Usually, the baby’s head is down toward the birth canal. The baby is about 18 to 20 inches long and weighs about 7 pounds.
CLASSWORK 2
1. What is pregnancy?
2. Give four facts about pregnancy
ASSIGNMENT 2
SECTION A
1. The following are not symptoms of pregnancy in human except (a) fighting (b) fatigue (c) crying (d) walking
2. The ideal pregnancy duration in human is (a) 6 months (b) 7 months (c) 8 months (d) 9 months
3. The fusion of the male and female gamete to form a zygote is known as (a) conception (b) fertilization (c) menopause (d) menstruation
4. The fluid that cushions the growing embryo is called (a) water (b) mineral (c) amniotic fluid (d) baby fluid
5. Pregnancy can be detected with any of these symptoms except (a) nausea (b) fatigue (c) food aversion (d) menstruation
SECTION B
1. Carefully state the difference between fertilization and conception
2. Mention any four signs and symptoms of pregnancy
3. Mention three ways of detecting pregnancy
WEEK THREE
FORCE
v Meaning
v Types of Force
v Contact and non-contact force
v Magnetic and gravitational force
Meaning
A force can be defined as any action that makes or tries to move, stop or alter the speed of a body in a given direction. Force can also be said to mean a push or a pull. The unit of force is Newton (N). Force is given by the formula:
Force (F) = Mass (m) x Acceleration (a)
F = ma
Types of Force
There are two types of force namely:
1. Contact force
2. Non-contact
Contact and non-contact force
1. CONTACT FORCES: These are forces which sources are in contact with the body to which they are applied. The contact forces could be direct or indirect. Examples of contact forces are: push, pull, tension, friction, upthrust
2. NON- CONTACT FORCES: These are forces which the sources do not require contact with the body they are applied. These forces act through a region in space called field. They are therefore also called force fields. Examples include magnetic force, gravitational force and electric force
Magnetic and gravitational force
1. MAGNETIC FORCE: In a bar magnetic, there is North Pole end south pole end. The like poles repel each other while unlike poles attract each other.
Magnets can attract other magnets, iron fillings or any other metallic materials. This phenomenon show that a magnetic force acts over an area around the magnet. Thus a magnetic force is called a field force which acts over an area.
2. GRAVITATIONAL FORCE: The force which the earth attracts all objects to itself is called the force of gravity or gravitational force. This is the reason why objects above the earth fall down to the earth.
3. ELECTRIC FORCE: Electric force field exists between two electric charges. Unlike charges attract each other while like charges repel each other.
CLASSWORK 3
1. What is force? Give the SI unit
2. State two contact force
ASSIGNMENT 3
SECTION A
1. The correct SI unit of force is (a) Joules (b) Watt (c) Newton (d) Metre
2. Which of the following statement is false (a) a force changes the shape of a body (b) forces may be balanced or unbalanced (c) a force cannot change the direction of a moving body (d) a force changes the speed of object
3. The gravitational force can be found (a) on the earth (b) in the moon (c) around the planets (d) in the galaxy
4. The magnetic force is also known as _________(a) pulse ( b) electrical (c) field force (d) gravitational force
5. Which of the following is a type of force (a) electrical (b) heat (c) rotating (d) reversible
SECTION B
1. Mention three non-contact force that you know
2. State two importance of force
3. State the difference between contact and non-contact force
WEEK FOUR
CALCULATION OF GRAVITATIONAL FORCE
v Calculation of gravitational force
v Balanced and unbalanced forces
v Frictional force
v Uses/Advantages
v Disadvantages
Calculation of gravitational force
CALCULATION OF WORK DONE AGAINST GRAVITY
Suppose you lift an object of mass 1kg from the ground to a height of 1m, the work done in lifting the abject is calculated by using the formula; Mgh
Mgh = 1 x 1 x 9.8 joules (g = 9.8m/s2)
Joule is the unit of work done.
Balanced and unbalanced forces
When an object is stationary, the forces acting on it are balanced forces. The sum of such forces acting on the body is zero and they act in opposite direction.
When an object is in motion (moving), the forces acting on it are unbalanced. The sum of such forces is not zero. Such forces are either acting in it are direction or the same direction but are not equal in value. Unbalance forces cause a body to accelerate.
GENERAL EFFECT OF A FORCE
1. A force causes motion of an object
2. A force causes moving object to come to rest (stop)
3. A force changes the speed of a body in motion
4. A force causes changes in the direction of motion.
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
TO GET YOUR COMPLETE LESSON NOTE AT AN AFFORDABLE PRICE, HIT THE WHATSAPP BUTTON BELOW