Social Studies Primary 4
CLICK HERE TO ACCESS CIVIC PRIMARY 4 FIRST TERM LESSON NOTE
SOCIAL STUDIES – PRIMARY 4 – FIRST TERM
WEEKLY TOPICS
- Living in the family
- Relationship of some members of the family
- Marriage
- Marriage problems and solutions
- Our culture and elements of culture
- Culture
- Culture
-
- Ways of cultural preservation, e.g., museums, symbols, buildings, dressing, festivals
- Some cultural practices to be discarded, like ritual killings and tribalism, with reasons
- Cultural values to be retained, e.g., respect for elders, hard work, and high moral values
- Our Religion
- What is Religion?
- Types of Religion
- Modes of worship in different religious practices
- Materials used in worship, e.g., candles, music, the Holy Bible, beads, the Quran
- Religious Practice (Lagos State Ministry of Education Schemes of Work for Primary Schools)
- Islamic Religion: Belief in Allah and Prophet Mohammed as the messenger, praying five times a day, and worshipping in the mosque.
- Traditional Religion: Idol worshippers who practice in shrines and believe in some objects as their god.
- Christian Religion: Belief in the Supreme Being called God and His only begotten Son, Jesus Christ. Christians worship in the church on Sundays and use the Holy Bible to pray.
- Similarities and aspects of religion
- We all pray to God through different means.
- Differences in religion, including styles of dressing.
11. Other people’s beliefs and traditions
- Ways in which traditions differ and are similar.
- Different names for God.
- Methods of worship.
WEEKS 1 & 2 – TOPIC: LIVING IN THE FAMILY
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
- Identify types of families
- Understand the duties of family members
- Explain the importance of family
- Describe relationships between family members
- Understand the benefits of family
ENTRY BEHAVIOR / PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE
The students are familiar with the concept of family.
REFERENCE MATERIALS
- NERDC Basic Education Curriculum for Primary Schools
- Lagos State Scheme of Work
- Unified Schemes of Work for Primary Schools (Middle Basic)
- Internet resources
- Social Studies textbooks for Primary Schools
- Nigeria Educational Research and Development Council Scheme (NERDC)
CONTENT
FAMILY
A family is a social unit living together.
MEMBERS OF THE FAMILY
The family is the first stage of human interaction. It is the first recognized social unit in every society. Families bring people together and help in the growth of society.
The members of a family include the father, mother, and children (if there are any).
Families are divided into two types:
- Nuclear Family
- Extended Family
MEMBERS OF A NUCLEAR FAMILY
A nuclear family consists of a father, a mother (or mothers), and children (if there are any). The nuclear family of a married man includes his wife and children. Similarly, a married woman’s nuclear family consists of her husband and children. For a boy or girl, the nuclear family includes parents, brothers, and sisters.
In other words, a nuclear family consists of a mother, a father, and their children. This form of family exists worldwide. It is also called the simple family, and it is the smallest family unit.

MEMBERS OF AN EXTENDED FAMILY
An extended family consists of multiple families that are related by blood. In other words, an extended family is a combination of different nuclear families.
Members of an extended family include:
- Grandparents (grandfather and grandmother)
- Parents (father and mother)
- Siblings (brothers and sisters)
- Uncles and Aunts (father’s and mother’s siblings)
- Cousins (children of uncles and aunts)
- Nephews and Nieces (children of one’s siblings)
The extended family is a family unit that includes parents and children, along with grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, and sometimes even more distant relatives.
For example, you belong to the family your father came from, and at the same time, you are part of the family your mother came from. This means you are a member of an extended family.
The extended family system is common in all ethnic groups in Nigeria. It is an important aspect of African culture and tradition, promoting unity, support, and strong family bonds.

Family tree
The family tree gives a simple picture of who the members of the extended family are, and how they are related to one another.
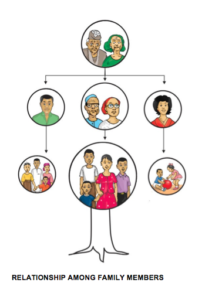
RELATIONSHIP AMONG FAMILY MEMBERS
Family members share a special bond and have common connections. Some of these relationships include:
- They have the same family name.
- They speak the same language.
- They come from the same state.
- They originate from the same village.
BENEFITS OF FAMILY RELATIONSHIPS
Family relationships provide numerous benefits, including:
- Helping one another.
- Providing assistance in times of need.
- Showing love and concern for one another.
- Offering advice and guidance.
- Supporting each other emotionally and financially.
- Ensuring protection and security for one another.
- Building a strong family bond.
FAMILY RESPONSIBILITIES
Responsibilities of Parents to Their Children and Wards
Parents have essential responsibilities in caring for their children and wards, including:
- Providing Basic Needs – Parents ensure their children have food, clothing, and shelter.
- Education and Training – Parents invest in their children’s education by:
-
- Sending them to school.
- Paying school fees.
- Buying essential school materials such as bags, shoes, uniforms, and books.
- Encouraging them to study at home to perform well in school.
Would you like me to add more details or refine anything further? 😊

3 Parents name their children when they are born. They give them the kind of names people bear in their family. Sometimes the name shows what parents want the child to become.
4 They teach them to be of good behaviour and to respect elders, thereby contributing to their moral development.
5 Parents protect their children from sickness and danger. However, they take their children and wards to the hospital for treatment when they are sick.

6 They advise and teach their children and wards on how to do things properly. For example, mothers teach their daughters and even sons how to cook and clean the house. Fathers may teach their children how to do farm work or how to fix and repair things in the house. If children grow up without parents or guardians to guide them well, they may not be able to learn those things that will make them good and responsible citizens.


RESPONSIBILITIES OF CHILDREN TO THEIR PARENTS
Children and other young members of the family help the parents in the following ways:
1 They go on errands for their parents.
2 They do domestic work such as washing clothes, cooking, sweeping, dusting, and taking care of the younger ones.
Children also have responsibilities towards their parents, including:
3. Helping their parents with business activities, such as selling goods if their parents are traders.
4. Taking care of their parents when they are sick.
INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURE
1. The teacher revises the previous lesson.
2. The teacher introduces the new topic.
3. The teacher explains the lesson in detail.
STUDENT ACTIVITIES
· Students mention members of their family.
EVALUATIVE ACTIVITIES
1. Define family.
2. Family is divided into _____.
3. Mention the types of family.
4. Mention three effects of tobacco abuse.
5. Mention three effects of cannabis abuse.
CONCLUSION
The teacher summarizes the lesson.
WEEK 3
TOPIC: MARRIAGE
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
· Define marriage.
· Identify types of marriage.
· Understand marriage practices in Nigeria and how they differ across communities.
· Discuss marriage problems and their solutions.
REFERENCE MATERIALS
· NERDC Basic Education Curriculum for Primary Schools
· Lagos State Scheme of Work
· Unified Schemes of Work for Primary Schools (Middle Basic)
· Internet resources
· Nigeria Educational Research and Development Council Scheme (NERDC)
· Social Studies Textbooks for Primary Schools
ENTRY BEHAVIOR / PREVIOUS LESSON
Students are already familiar with the Relationship of Some Members of the Family.
CONTENT
MARRIAGE
Marriage is the state of being a married couple, voluntarily joined for life (or until divorce). It is the union of a man and a woman to become husband and wife.
Marriage involves arrangements and ceremonies that society approves for a man and woman to come together and form a family.

TYPES OF MARRIAGE
The types of marriage in our society include:
1. Monogamous Marriage
2. Polygamous Marriage
MONOGAMOUS MARRIAGE
A monogamous marriage is a union between one man and one wife. This means a person has only one spouse (partner) at a time. This type of marriage is commonly practiced among Christians.
POLYGAMOUS MARRIAGE
A polygamous marriage is when a man marries more than one wife. A man can marry as many wives as he wants, but he must be capable of taking care of them. This practice is common among Muslims and traditional worshippers.
MARRIAGE PRACTICES IN NIGERIA AND THEIR DIFFERENCES
Marriage customs vary from one community to another.
MARRIAGE PRACTICES AMONG THE HAUSA (NORTHERN NIGERIA)
1. When a Hausa boy sees a girl he loves, he informs his parents.
2. His parents meet with the girl’s parents to express interest in marriage.
3. If the girl’s parents agree, the boy starts visiting the girl’s house and may give her gifts.
4. The boy’s parents and the girl’s parents agree on a wedding date.
MARRIAGE PRACTICES AMONG THE YORUBA (WESTERN NIGERIA)
1. When a young man wants to marry a girl, his parents hire a negotiator to speak with the girl’s parents.
2. In some cases, marriage discussions begin when the girl is still young.
MARRIAGE PRACTICES AMONG THE IGBO (EASTERN NIGERIA)
1. When a young man sees a girl he loves, he informs his parents.
2. His parents conduct inquiries about the girl’s family to ensure they have good morals.
REASONS WHY MARRIAGE PRACTICES DIFFER ACROSS COMMUNITIES
1. Religion – Different religious beliefs influence marriage customs.
2. Culture – Traditional customs and values affect marriage practices.
WHY MARRIAGE PRACTICES SHOULD CONTINUE
1. It promotes unity.
2. It preserves culture.
3. It encourages mutual understanding.
CHANGES IN MARRIAGE PRACTICES
1. Influence of foreign culture.
2. Impact of Western education.
3. Some outdated traditional practices are being abandoned.
4. Cost of living has affected marriage customs.
DIFFERENCES IN MARRIAGE PRACTICES ACROSS COMMUNITIES
· Traditional communities often practice polygamy, where a man can marry multiple wives and is responsible for caring for them.
· Muslims are allowed to practice polygamy, with a maximum of four wives.
· Christians and most urban dwellers practice monogamy, where a man marries only one wife and provides for her and their children.
INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURE
1. The teacher revises the previous lesson.
2. The teacher introduces the new topic.
3. The teacher explains the lesson.
EVALUATIVE ACTIVITIES
1. Define marriage.
2. Mention the types of marriage.
3. List three reasons why marriage practices differ across communities.
4. Mention three changes that have taken place in marriage practices.
CONCLUSION
The teacher summarizes the lesson.
WEEK 4
TOPIC: MARRIAGE PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS (MARRIAGE FAILURE)
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
· Define marriage.
· Identify types of marriage.
· Explain different marriage practices in Nigeria.
· Discuss marriage problems and their solutions.
REFERENCE MATERIALS
· NERDC Basic Education Curriculum for Primary Schools
· Lagos State Scheme of Work
· Unified Schemes of Work for Primary Schools (Middle Basic)
· Internet resources
· Social Studies Textbooks for Primary Schools
ENTRY BEHAVIOR / PREVIOUS LESSON
Students are already familiar with marriage and its types.
PROBLEMS OF LIVING TOGETHER IN MARRIAGE
1. People have different likes and dislikes.
2. People have different ways of thinking.
CAUSES OF DISAGREEMENTS IN MARRIAGE
1. Lack of money
2. Misunderstandings
3. Influence of friends (gossiping)
4. Problems from in-laws
5. Infertility

TOPIC: MARRIAGE PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS (MARRIAGE FAILURE)
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
At the end of this lesson, pupils should be able to:
· Define marriage.
· Identify types of marriage.
· Explain different marriage practices in Nigeria.
· Discuss marriage problems and their solutions.
REFERENCE MATERIALS
· NERDC Basic Education Curriculum for Primary Schools
· Lagos State Scheme of Work
· Unified Schemes of Work for Primary Schools (Middle Basic)
· Internet resources
· Social Studies Textbooks for Primary Schools
ENTRY BEHAVIOR / PREVIOUS LESSON
Students are already familiar with marriage and its types.
PROBLEMS OF LIVING TOGETHER IN MARRIAGE
1. Differences in likes and dislikes
2. Different ways of thinking
3. Causes of disagreements in marriage:
· Lack of money
· Misunderstanding
· Influence of friends (gossiping)
· Problems from in-laws
· Infertility
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS IN MARRIAGE
1. Both partners should be honest with each other.
2. They should show love and care through sharing and understanding.
3. They should listen to each other.
4. They should practice patience.
5. They should tolerate each other’s weaknesses.
6. They should respect each other’s views.
7. They should cooperate and plan together.
INSTRUCTIONAL PROCEDURE
1. The teacher revises the previous lesson.
2. The teacher introduces the new topic.
3. The teacher explains the lesson.
EVALUATIVE ACTIVITIES
1. Mention three problems in marriage.
2. Mention three solutions to marriage problems.
CONCLUSION
The teacher summarizes the lesson.

Pingback: agric Primary 4 First Term Lesson Note - Edureservoir.com