Home Econs Lesson notes for primary 4 Third Term
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
THIRD TERM HOME ECONOMICS PRIMARY FOUR
SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK1 REVISION OF LAST TERM
WEEK2 SEWING BASIC STITCHES: DEFINITION AND TYPES OF STITCHES
WEEK 3 SEWING BEASIC STITCHES: PERMANENT STITCHES
WEEK4 PROCESS OF BASIC STITCHES:
WEEK5 SIMPLE DECORATIVE STITCHES
WEEK6 PRACTICAL DECORATIVE STITCHES ON BROWN PAPER: SATIN STITCHES
WEEK7 MAKING SIMPLE DECORATIVE STITCHES ON BROWN PAPER
WEEK 8 MAKING BLANKET OR LOOP STITCHES
WEEK9 SIMPLE CLOTHING CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES SEAM
WEEK10 RUN AND FELL
WEEK11 USES OF PLAIN SEAM
WEEK 2
TOPIC: SEWING BASIC STITCHES
SUBTOPIC: DEFINITION AND TYPES OF STITCHES
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: AT THE END OF THE LESSON, PUPILS SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
1. Define stitches
ii. Name the types of stitches
iii. Explain the types of stitches.
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS:
A Chart showing different stitches.
Piece of fabrics for sewing stitches
Tailor chalk, Fabrics, Measuring tape etc
RESOURCES AND MATERIALS:
Scheme of work
All relevant materials
9-Years Basic Education Curriculum
Online information
BUILDING BACKGROUND/CONNECTION TO PRIOR KNOWLEDGE: Pupils are familiar with the topic in their previous classes.
CONTENT OF THE LESSON
DEFINITION OF STITCHES
A stitch is the journey of two pieces of materials with a line of stitch. Stitches means the movement of thread and needle in and out of the stitches.
MATERIALS NEEDED FOR STITCHES
Needle
Thread
Scissors
Ruler
Tailor’s chalk or marking pencil
Straight pin
TYPES OF STITCHES
1. Temporary stitches
2. Permanent stitches
TEMPORARY STITCHES
Temporary stitches are used for joining materials temporarily before the permanent stitch is made. It is
worked from right to left, starting with a knot in a contrasting color thread, so that it can be easily
removed.
Tacking or basting is a temporary stitch used for holding two or more layers of
fabric together before a permanent stitch in made. Usually the stitch is worked
from right to left, starting with a knot in a contrasting color thread, so that it can be
easily removed.
PROCESS OF BASIC STITCHES
1. Even tacking
2. Uneven tacking
3. Diagonal tacking
4. Tailor’s tacking
1. Even Tacking:
Use a thin needle and start the stitch with a knot. The stitches are of equal length about on both sides of the material. Much number of longer stitches can be done at a time. This is used for tacking seams & other details which must be held securely.
2. Uneven Tacking:
In this, the stitches on the upper side is or at least twice that on the underside. This stitch can be used for longer folds & seams. This is comparatively stronger than even tacking. Use this type of tacking as a guideline or where there is little or no strain.
3. Diagonal Tacking:
While attaching two or more layer of fabrics this type of stitch is made about apart before making machine stitch.
Work stitches through the material at right angles to the fabric edge so that a diagonal or slanting stitch in made on the upper side and a vertical stitch is made on the under side.
4. Tailor’s Tacking:
Start tacking using double thread of contrasting color, so that they can be easily seen. Tack through double layer of fabric along the seam lines using even stitches of length apart, leave them as loop without pulling it tight. After completing, raise the upper layer of fabric slightly and clip the thread between the layers. So that the thread tufts, will remain on both the layers of fabric and remain as a guide line. This is especially used for marking details between patterns such as dart markings and pleat markings.
STRATEGIES AND ACTIVITIES
STEP I; The Teacher revises the previous week lesson.
STEPII: The Teacher introduces the new topic.
STEP III: The Teacher explains the note in details.
STEPIV: The Teacher gives room for pupils to ask questions.
STEPV: The Teacher evaluates the pupils.
ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION
1. Define stitches
ii. Name the types of stitches
iii. Explain the types of stitches
WRAP-UP(CONCLUSION)
Teacher goes over the topic once again to enhance better understanding.
ASSIGNMENT
List and explain the types of temporary stitches.
WEEK3
TOPIC: SEWING BASIC STITCHES
SUBTOPIC: PERMANENT STITCHES
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: AT THE END OF THE LESSON, PUPILS SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
1. Define stitches
ii. Name the types of stitches
iii. Explain the types Of permanent stitches.
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS:
A Chart showing different stitches.
Piece of fabrics for sewing stitches
Tailor chalk, Fabrics, Measuring tape etc
RESOURCES AND MATERIALS:
Scheme of work
All relevant materials
9-Years Basic Education Curriculum
Online information
BUILDING BACKGROUND/CONNECTION TO PRIOR KNOWLEDGE: Pupils are familiar with the topic in their previous classes.
CONTENT OF THE LESSON
PERMANENT STITCHES
These stitches are made permanent on the fabric and need not be removed later like Temporary stitches. The stitching works from left to right ‘taking a small stitch; then insert the needle at the end of the previous stitch; bringing it out beyond where the thread emerges. Continue always at the end of the previous stitch.
Some of permanent stitches are 1. Running stitch 2.Back stitch 3. Run and back stitch 4. Hemming stitch 5. Whipping stitch.
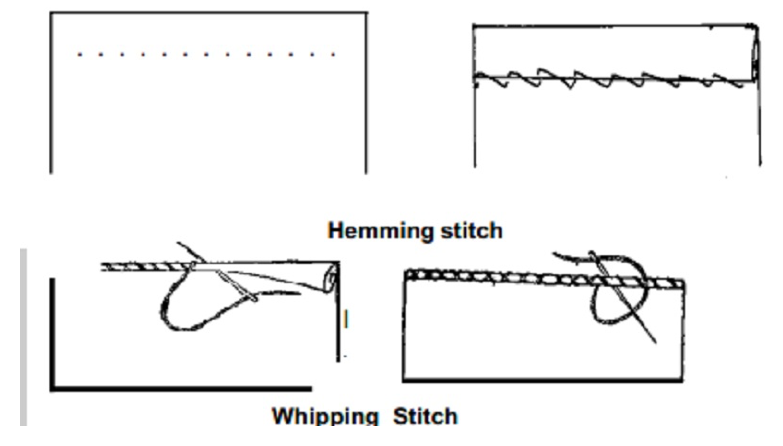
1. Running Stitch: This is the simplest form of hand stitch which is used for permanent sewing stitched using same color thread. Hand made seams, darning, gathering and finishing edges can be done with this stitch. It is similar to even basting, but the stitches are much smaller, straight, fine and evenly spaced. It is comparatively easy and can be worked fast.
2. Back stitch: The is strong and sometimes substituted for machine stitch. It takes much time. Care must be taken while stitching, since stitching is done on the right side of the fabric. On the wrong side of the fabric the stitch is similar to stem stitch. Stitches should be about 1/8′ long on the Back Stitch right side. To make the back stitch, push needle up through the material at a point on the stitching line about 1/8′ from its right end. Take a stitch inserting the needle 1/8′ back of the thread at the beginning of the stitching line and bringing it out an equal distance in the front of the thread. Repeat this way, keeping stitches uniform in size and fairly firm.
3. Run and back or Combination stitch: This stitch is similar to back stitch. This is used whose back stitch is not compulsory. A back stitch and two running stitches are combined and used for working plain seam done by hand. This stitch is faster than back stitch and stronger than the running stitch.
4. Hemming stitch: This is used to finish the raw edge of the garment usually referred as the hem. Hemming must be fine, evenly spaced and must be inconspicuous from the right side of the garment. Start the hem with a tiny knot and finish with the same. Hemming must be as invisible as possible on the right side. Of the garment do slanting stitch on wrong side, close enough to hold the hem securely, picking one or two yarns of the fabric. Usually this stitch is seen in all types of garments. Improperly hemmed garment may show problem as:
Hemming stitch
1.Stitches straightly formed
2.Puckered hem
3.Stitches not evenly spaced
4. Knot prominently shown on right side
5. Attached thread shown on right side
This stitch is used for finishing sleeve edges, handkerchief, skirt, hemline, neckline edges, piping, pillow covers and other edges also.
5. Whipping stitch:
This stitch is used to finish raw edges of fabrics and also in sleeves, collar of kid’s wear. The other name for this stitch is overcasing and rolled hem. Whipping produces slanting stitches taking stitches over the rolled fabric edge with needle in a straight position.
Do stitching from right hand side of the fabric till the left end. After completing, start from the left end, inserting the needle on the same point where the stitch is already formed. Continue the same way from the left to right end. The finished fabric gives continuous ‘X’ shape stitches. On both the sides stitches appear similar in shape.
Decorative Stitches
STRATEGIES AND ACTIVITIES
STEP I; The Teacher revises the previous week lesson.
STEPII: The Teacher introduces the new topic.
STEP III: The Teacher explains the note in details.
STEPIV: The Teacher gives room for pupils to ask questions.
STEPV: The Teacher evaluates the pupils.
ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION
1. Define stitches
ii. Name the types of stitches
iii. Explain the types of Permanent stitches
WRAP-UP(CONCLUSION)
Teacher goes over the topic once again to enhance better understanding.
ASSIGNMENT
1. Define permanent stitches
2. What are the guidelines for making permanent stitches
3. Explain whipping and back stitches
WEEK 4
TOPIC: SEWING BASIC STITCHES
SUBTOPIC:PROCESS OF BASIC STITCHES
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: AT THE END OF THE LESSON, PUPILS SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
1. list the uses of permanent stitches
2. list the uses of temporary stitches
3. mention the process of basic stitches
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS:
Piece of fabrics for sewing stitches
Tailor chalk, Fabrics, Measuring tape etc
RESOURCES AND MATERIALS:
Scheme of work
All relevant materials
9-Years Basic Education Curriculum
Online information
BUILDING BACKGROUND/CONNECTION TO PRIOR KNOWLEDGE: Pupils are familiar with the topic in their previous classes.
CONTENT OF THE LESSON
PROCESS OF BASIC STITCHES
1. Even tacking
2. Uneven tacking
3. Diagonal tacking
4. Tailor’s tacking
1. Even Tacking:
Use a thin needle and start the stitch with a knot. The stitches are of equal length about on both sides of the material. Much number of longer stitches can be done at a time. This is used for tacking seams & other details which must be held securely.
2. Uneven Tacking:
In this, the stitches on the upper side is or at least twice that on the underside. This stitch can be used for longer folds & seams. This is comparatively stronger than even tacking. Use this type of tacking as a guideline or where there is little or no strain.
3. Diagonal Tacking:
While attaching two or more layer of fabrics this type of stitch is made about apart before making machine stitch.
Work stitches through the material at right angles to the fabric edge so that a diagonal or slanting stitch in made on the upper side and a vertical stitch is made on the under side.
4. Tailor’s Tacking:
Start tacking using double thread of contrasting color, so that they can be easily seen. Tack through double layer of fabric along the seam lines using even stitches of length apart, leave them as loop without pulling it tight. After completing, raise the upper layer of fabric slightly and clip the thread between the layers. So that the thread tufts, will remain on both the layers of fabric and remain as a guide line. This is especially used for marking details between patterns such as dart markings and pleat markings.
USES OF PERMANENT AND TEMPORARY STITCHES
PERMANENT STITCHES
1. It can be used as decorative stitches
2. It can be used to sew fabrics permanently
3. It can be used to hold down gown hem
TEMPORARY STITCHES
1. It can be used to hold side seam
2. To make gathers on fabrics
3. To hold materials in position temporarily
STRATEGIES AND ACTIVITIES
STEP I; The Teacher revises the previous week lesson.
STEPII: The Teacher introduces the new topic.
STEP III: The Teacher explains the note in details.
STEPIV: The Teacher gives room for pupils to ask questions.
STEPV: The Teacher evaluates the pupils.
ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATION
1. list the uses of permanent stitches
2. list the uses of temporary stitches
3. mention the process of basic stitches
WRAP-UP(CONCLUSION)
Teacher goes over the topic once again to enhance better understanding.
ASSIGNMENT
1……………………….. holds fabrics permanently?
2.temporary stitches is used to make…………………………..on fabrics
(a)feather (b) gathers(c)land
3. Mention 5 basic process of stitches.
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS