First Term English Lessons for Primary 5
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
BASIC 5 LESSON PLAN FOR 1ST TERM
WEEK: One
CLASS: Basic Five
SUBJECT: English language
TOPIC: Revision
BEHAVIOURAL OBJECTIVES:At the end of the lesson, pupils should be
able to answer questions on the previous topics
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL: Pictures, charts and textbook
REFERENCE MATERIAL: Nigeria Primary English. Book 5
BUILDING A BACKGROUND: Pupils are familiar with the revised topics
CONTENT:
REVISION
Write out the past tense of the following
1. Eat
2. Drink
3. Work
4. dance
5. cry
6. forget
WEEK: Two
CLASS: Basic Five
SUBJECT: English language
TOPIC: Reading: Teaching of New words, meaning and comprehension;
How i Spent My Last Holiday; The tenses.
BEHAVIOURAL OBJECTIVES:At the end of the lesson, pupils should be
able to:
i. Read and comprehend the passage
ii. Learn new words
iii. Use the correct forms of tenses in sentences
BUILDING A BACKGROUND: Pupils are familiar with comprehension
passages and new words
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL: Pictures, charts and textbook
REFERENCE MATERIAL: Nigeria Primary English. Book 5
CONTENT:
READING:
Now read the passage carefully and try to remember the facts in it.
CREATION MYTHS
A myth is an ancient story that explains something very important to people
in a particular region. Older people tell these stories to younger people in
every part of the world. All storytellers change these stories when they tell
them; so there are now many different versions of the same myth. Much later,
people began to write them down. A creation myth is a myth that explains
how the universe, the Earth or life began. There are hundreds of wonderful
creation myths in every country and region. Here are some from Nigeria. The
first example is a creation myth known to our Efik people. The creator,
Abassi, made a man and a woman but he did not want them to live on Earth.
His wife, Atai, persuaded him to let them be here. Abassi wanted to control
the humans, so he made them eat all their meals with him. He did not want
them to grow food or hunt. He also ordered them not to have children.
However, the woman was fed up and she began growing food. Then the man
joined his wife in the fields and they stopped coming to eat with Abassi. Soon
they had children. Abassi was very angry and blamed his wife for what
happened. She promised to do something about it. She sent death to Earth and
she also sent arguments and fighting to weaken the power of the people.
Use examples in the passage to choose the correct word from each pair in
brackets.
1 I’m writing (down/up) the names of friends I want to come to my party.
2 The story is known (to/about) children in this area.
3 There are millions of people living (in/on) Earth.
4 Bayo is fed (with/up) because he has no money for ice-cream.
5 He blamed me (for/by) missing the bus!
NEW WORDS
1. Ancient 2. Myth 3. Versions 4. Bored 5. Empty
GRAMMAR
Fill in the gaps with the most appropriate for of tenses.
1. She …………….. rice and beans last night. ( eat )
2. The old woman ……………. From the tree. ( fell )
3. My father ………………. a red jeep. ( drive)
4. Who ……………… the flower vase? ( break )
5. She ………….. rice and beans. ( prepare)
EVALUATION: Pupils are evaluated thus:
Write a composition on the topic ‘ How I Spent My Last Holiday
“WEEK: Three
CLASS: Basic Five
SUBJECT: English language
TOPIC: A. Speech work: Sentences in the passive voice ‘with and without
an agent’
B. Structure: Mastering of the passive voice Construction change
active sentences into Passive voice
C. Grammar: Relative clauses using words such as “who”, “which”,
and “that”
D. Writing: Writing abbreviated forms of letters e.g. Telegrams
format/content
BEHAVIOURAL OBJECTIVES:At the end of the lesson, pupils should be
able to:
i. Change sentences in active voice to passive voice
ii. Correctly use ‘who’, ‘which’, ‘that’
iii. Write abbreviated forms of letter
BUILDING A BACKGROUND: Pupils are familiar with abbreviated forms
of letters and construction of sentences in active and passive voices
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL: Pictures, charts and textbook
REFERENCE MATERIAL: Nigeria Primary English. Book 5
CONTENT:
STRUCTURE
Active and Passive voice
In active voice, the subject performs the action and the action is received by
the object. E.g:
1. I ran into the class.
2. Dupe took the lunch box.
Passive verbs tell us about the person or thing that the action in a sentence is
happening to. It is not always clear who or what is doing the action, as in:
1. The car was stolen.
2. We do not know who stole the car.
GRAMMAR
Relative Clause using ‘Who’, ‘Which’ and ‘That’
Relative clauses are used to join two or more sentences together using
‘who’, ‘which’, and ‘that’
Examples:
1. This is my aunt. She is staying with us.
This is my aunt who is staying with us.
2. Next weekend is the party. I told you about it.
Next weekend is the party which i told you about.
3. Here is the book. I promised to give it to you.
Here is the book which i promised to give you
WRITING
ABBREVIATED FORMS OF LETTER
An abbreviated form of letter is a short form of letter usually in form of a
telegram or a text message. It doesn’t contain addresses titles etc.
Examples:
Daddy, please bring my books. Am in school.
Tomorrow is my birthday. 9am prompt. Be punctual
I will be absent in school today because am not feeling well. Tell my teacher.
EVALUATION: Pupils are evaluated thus:
Write these pairs of sentences as one sentence using ‘who’, ‘which’, or ‘that’.
1 There’s the boy. He broke the window.
2 That’s the old woman. She helped the infant up when he fell down.
3 Is that the bike? You got it for your birthday.
4 Can I borrow the magazine? You bought it this morning.
5 Have you watched the DVD? I lent it to you last week.
WEEK: Four
CLASS: Basic Five
SUBJECT: English language
TOPIC: A. Speech Work: Intonation practice in statement Questions
command and request
B. Reading: Teaching of new words meaning and Comprehension
C. Grammar: Paragraphs major and minor Characters
D. Writing: My best friend
BEHAVIOURAL OBJECTIVES:At the end of the lesson, pupils should be
able to:
i. Use the correct intonation in statements, command and request
ii. Learn new words
iii. Explain the concept of major and minor characters
iv. Write a composition on the topic ‘My Best Friend’
BUILDING A BACKGROUND: Pupils are familiar with intonation and
composition writing
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL: Pictures, charts and textbook
REFERENCE MATERIAL: Nigeria Primary English. Book 5
CONTENT:
INTONATION IN STATEMENTS, COMMAND AND REQUEST
Intonation has to do with the falling and rising of our reading tone.
Example:
Is there a snake on the kitchen floor? ( Yes/No Question)
No, there isn’t. ( Statement)
May i use the bathroom please? ( Request)
When are you going home? (Question)
GRAMMAR
MAJOR AND MINOR CHARACTERS
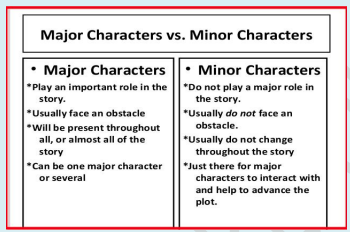
EVALUATION: Pupils are evaluated thus:
Using an arrow, indicate the appropriate intonation for each of these
sentences.
1. Do we have some sugar at home?
2. Where is my school bag?
3. I need to rest.
4. Can i have some stew?
5. Are you going home now?
WEEK: Five
CLASS: Basic Five
SUBJECT: English language
TOPIC: Speech Work: Reading poem on good Neighborliness; Reading:
Teaching of new words meanings and Comprehension; Grammar: Formal
letter to a village head or any Other constituted authority; Writing: Features
of formal and informal letters
BEHAVIOURAL OBJECTIVES:At the end of the lesson, pupils should be
able to:
i. Read and comprehend a poem
ii. Learn new words
iii. State the features of a formal letter
iv. Write a formal letter
BUILDING A BACKGROUND: Pupils are familiar with letter writing and
poems
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL: Pictures, charts and textbook
REFERENCE MATERIAL: Nigeria Primary English. Book 5
CONTENT:
Speech Work
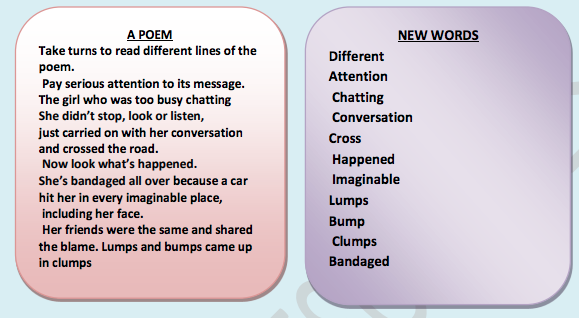
Writing
FEATURES OF FORMAL AND INFORMAL LETTERS
EVALUATION: Pupils are evaluated thus:
A. Find the dictionary meaning of these words and use each of them in a
sentence
1. Different
2. Attention
3. Chatting
4. Conversation
5. Cross
6. Happened
7. Imaginable
8. Lumps
9. Bump
10.Clumps
B. Write a letter to your village head requesting that the road to your village
be repaired.
C. What are the differences between a formal letter and an informal letter
