Third Term Agric Science Lesson Note for JSS2
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
FISHERY
CONTENT
- Definition of Fishery
- Examples of Fish
- Classification of Fish
- Other Types of Aquatic Organisms
Definition of Fishery
Fishery refers to the management and production of fish and other aquatic animals. Of all animals living in water, fish is the most plentiful of them. Fish belongs to the group of aquatic vertebrates i.e. they have back bones. They are specially adapted to live, raised and reproduced in water.
The shape of their body enables them to move easily in water; swim bladder helps them to maintain their balance while the gills are used for respiration. All aquatic animals are found in water bodies such as lakes, pond, streams, rivers, oceans, lagoons and swamps. Other aquatic animals include whales, dolphins, shrimps, lobster, hippopotamus etc.
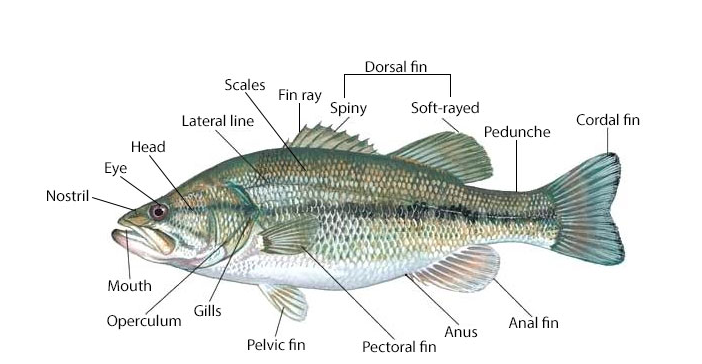
Parts of a Fish (Diagram)
Examples of Fish
Some examples of fish are:
- Cat fish
- Mud fish
- Nile perch
- Rays
- Shark
- Mackerel
- carps tilapia
- Croaker etc.

Classification of Fish
Fish can be classified into two based on (i) habitat and (ii) morphology (structure).
Classification of Fish based on Habitat
1. Fresh water fish
These are fish that can successfully live and reproduce only in salt free water such as ponds, lakes, streams, rivers, swamps etc. Examples of fresh water fish are tilapia, cat fish, Nile perch, mud fish, dogfish, moon fish, etc.

2. Salt water fish
These are fish which can live and reproduce successfully in saline (salt) water like lagoons, oceans, and seas. Examples are dog fish, shark, croaker, sole, and mackerel e.t.c.

Classification based on Morphology
1. Bony fish
These are fish that have the structure of their body made up of bones e.g. tilapia, carps, cat fish, croaker, mackerel, etc.
2. Cartilaginous fish
These are fish which have the structure of their body made up of cartilage e.g. dog fish, rays, shark, etc.
Other Types of Aquatic Organisms
There are many other organisms that are living inside water, apart from fish which are used as food by man. These include;
- Crustaceans (shell fish): Such as prawns, shrimps, crayfish, lobsters and crabs.
- Reptiles: Such as river snake, turtles, and crocodiles.
- Mammals: Such whales, Hippopotamus, dolphins, seals and porpoises.
- Molluscs (Snails): Such as river snails, periwinkle, oyster, squid, clam and octopus.

EVALUATION
- Define fishery.
- Enumerate two classifications of fish based on habitat.
- Enumerate two classifications of fish based on morphology.
- What are aquatic organisms?
- Give two examples each of the following: (i) Reptiles (ii) Molluscs (iii) Crustaceans
USES OF FISH AND FISH PRODUCTS/OTHER AQUATIC ORGANISMS
CONTENT
- Examples of Fish
- Fish Products
- Other Aquatic Food Organisms
- Uses of Fish, Fish Products and Other Aquatic Food Organisms
Examples of Fish
- Tilapia
- Cat fish
- Carp
- Shark
- Mud fish
- Croaker
- Mackerel
- Dog fish, Nile perch, etc.
Fish Products
Fish products include the following:
- Scales
- Fish skin,
- Oil
- Bones, etc.
Other Aquatic Food Organisms
- Whale
- Shrimps
- Seals
- Oyster
- Periwinkle, etc.
Uses of Fish, Fish Products and Other Aquatic Food Organisms
Fish is high in demand for health today because of low cholesterol (unsaturated fat) content. Fish and other aquatic food organisms are important source of animal proteins, minerals and vitamins essential for normal growth and development of the body. These are:
- They are sources of food.
- The skin of some aquatic organisms e.g. shark, whale etc. are used as fine leather for making bags shoes belts etc.
- Fish production provides raw materials for industries.
- Fishery provides employment opportunity for many people.
- Fish and its parts may be processed into fish meal which is an essential ingredient in most animal feeds.
- The shell of oyster and periwinkle are used for decorating the walls of some buildings.
- Unlike pork, beef, mutton and chevon, fish has no cultural or religious barriers.
- Some fish (coloured fish ) are used for aesthetic (beautification ) purpose in homes.
- The bones of fish can be crushed and processed into fertilizers.
- Fish ponds can provide entertainment as well as instructional facility for students of agriculture and fishery.
- Fish and other aquatic food organisms are taken today by many because of low cholesterol level which help in reducing high blood pressure and obesity.
EVALUATION
- List six importance of fish to man
- State four products of fish that are of economic importance.
- List three categorize of other aquatic organisms apart from fish and give two examples each.
SYSTEMS/METHODS OF FISHERY
CONTENT
- Systems of Fishery
Systems of Fishery
There are THREE major systems of fisheries in Nigeria. These are:
- Small scale fisheries
- Large scale fisheries (industrial fisheries)
- Aquaculture
Small Scale Fisheries
This is commonly practiced by local fishermen who live in fishing camps along the banks of the rivers, ponds or streams or along the coast of the sea. Small scale fisheries are very important because between 50-90% of all the fish consumed in the country come from it. Some of the features of small scale fisheries include:
- The fisher folks use simple equipment.
- They catch the fish by simple methods
- They catch small quantity of fish.
Large Scale or Industrial Fishery
This practice involves catching fish using large boat called TRAWLERS from natural water bodies. It is carried out on large inland rivers lakes and in the oceans. Large scale fisheries have the following features:
- It involves the use of complicated and expensive equipment.
- It is expensive to set up and operate.
- It is carried out in the sea/ocean or in very large inland lakes.
- A large quantity of aquatic animals are caught.
Aquaculture
This is otherwise known as fish farming. It is the practice of rearing fish and other aquatic organisms in artificial water bodies known as fish ponds. Aquaculture majorly produces fish in large quantity for eating and also produces beautiful coloured fish for home aquaria.
EVALUATION
- List and explain three (3) major systems of fishery in Nigeria.
PRESERVATION OF FISH
CONTENT
- Meaning of Fish Preservation
- Methods of Fish Preservation
Meaning of Fish Preservation
Fish preservation is the way of taking good care of fish after it has been captured in order to prevent it from going bad. Methods of preserving fish include the following:
Methods of Fish Preservation
- Sun drying: Removes water by evaporation and its cheap.
- Salting: Removes water and usually combine with other methods.
- Smoking: One of the oldest methods, adds taste and flavor.
- Freezing/refrigeration: Modern method, fish remain fresh no weight loss.
- Canning: It can last for a long period of time in cans.
- Oven-drying.
- Frying.
- Conversion to fish meal.
TO GET YOUR COMPLETE LESSON NOTE AT AN AFFORDABLE PRICE, HIT THE WHATSAPP BUTTON BELOW
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS