Mathematics Lesson notes for primary 3 Third Term
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
WEEK 1
Topic: Time
Behavioural Objectives: At the end of the lesson, pupils should be able to:
1. Give date in day and month
2. Mention the importance of time in our daily life.
CONTENT.
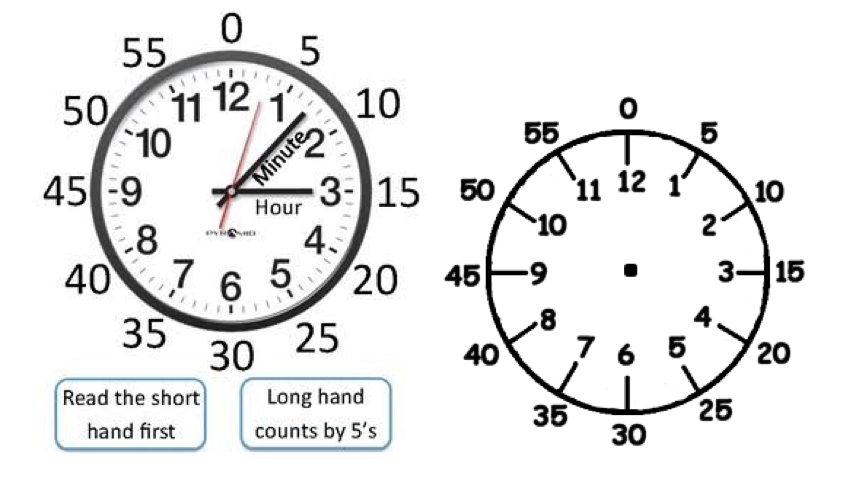
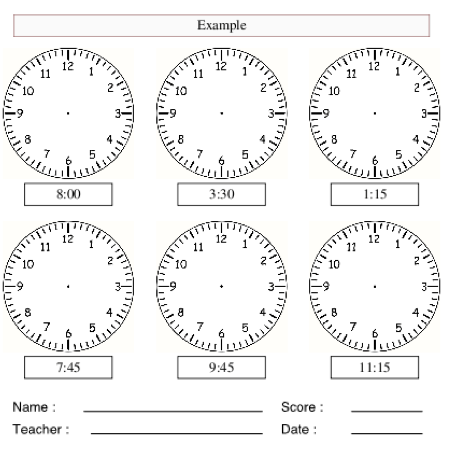
A clock is used to measure time. It has two hands: the hour hand and the minutes hand.
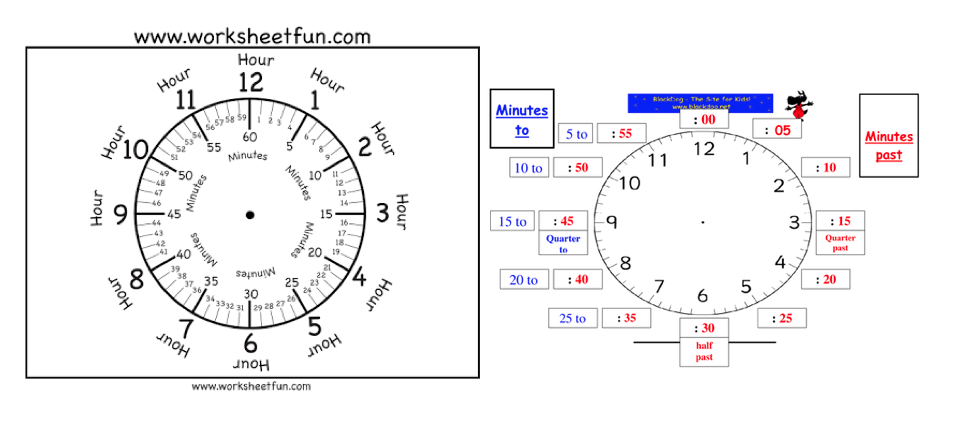

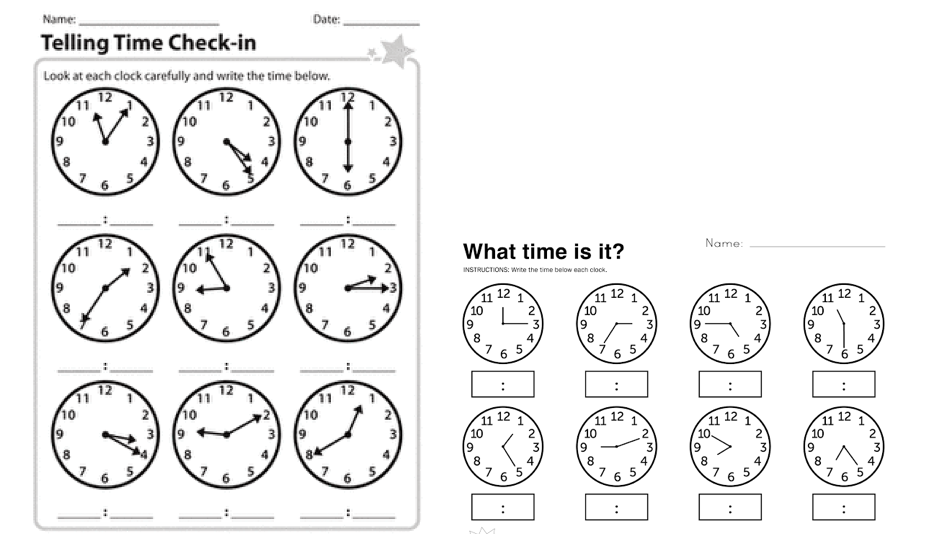
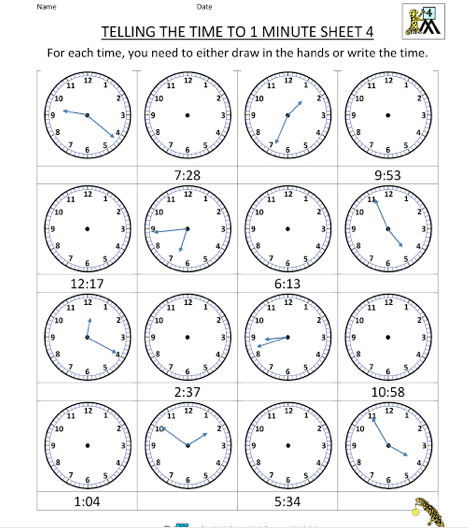
There are 60 minutes in 1 hour. There are twelve spaces from 12 to 12. When the minutes hand of the clock moves from 12 to 1, it covers one space and that space is worth 5 minutes. Since there are twelve spaces and one space is 5minutes. There are:
12×5=60 minutes in an hour.
When the minutes hand moves from 12 to 3 ,it covers three spaces. This is 15 minutes or one quarter of 60.
When the minutes hand moves from 12 to 6 spaces. This is 30 minutes or half of 60.





We use calendar to show the days of the week,months of the year and time of events within the year.
The diagram below shows the calendar for 2019 and 2017.
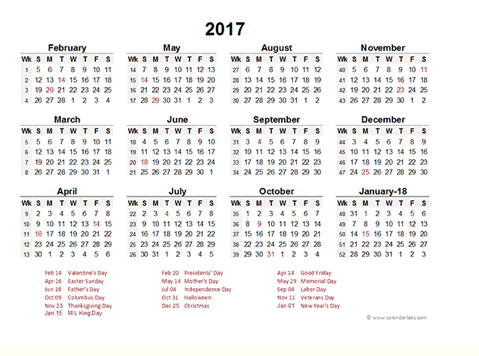




Exercise 1
Answer these questions using the calendar above.
1. What was the date of the last Friday of January?
2. On which day was Christmas celebrated?
3. Locate 27th of May in the calendar and write down what we celebrate
on that day.
4. Write the date for each of the last Saturdays of January to March.
5. Which month of the year has the least number of days?
6. How many months of the year have 31 days?
7. Write out two months of the year that have 30 days.
8. Find what the date was on the last Sunday of June.
9. How many days are there in the year 2015?
10. Was 2015 a leap year?
Exercise 2
1. What is the first day of the week?
2. What is the last day of the week?
3. Which is the last month of the year?
4. In which month do we celebrate Children’s Day?
5. Which month ends the first half of the year?
6. When is Nigerian Independence Day celebrated?
7. In which month do we celebrate New Year’s Day?
8. In which month is your birthday?
9. How many days are there in a leap year?
10. In which month is Democracy Day celebrated?
WEEK 2&4
Topic: Weight
Behavioural Objectives: At the end of the lesson, pupils should be able to:
Mention weight of objects in grams and kilograms
Make meaningful comparison of weight of objects like rocks,minerals.
CONTENT
COMPARING WEIGHT
A bottle of water weigh more than an empty bottle
A sister weighs less than a mug
A mathematics textbook weighs more than an exercise book.
Activity
A. Weigh the objects and record their weights in kilograms or grams.
1. 6 packets of whiteboard markers 2. 3 tins of Milo
3. 1 mathematics textbook 4. 1 bottle of water
5. 10 packets of pencils 6. 1 tin of milk
7. 1 bag of Semolina 8. 1 packet of biscuits
9. 2 big tins of Peak Milk
Standard units of weight
We need to use standard units to measure weight.
The kilogram (kg) is used as a unit when weighing heavy objects like
bags of rice, bags of cement, etc.
The gram (g) is used when weighing lighter objects like pencils, rulers, etc.
Measuring and estimating weight
These are different types of weighing scales
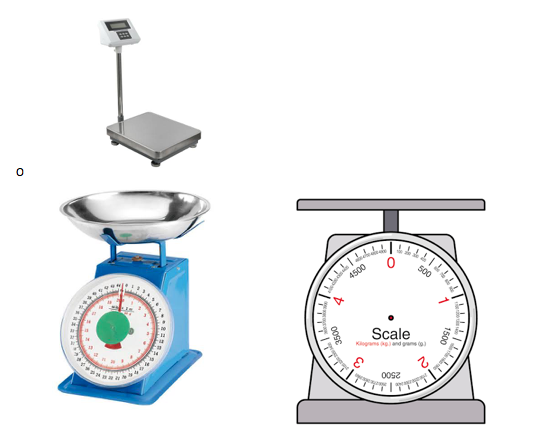
Exercise 2
Classify these objects according to their weight in grams and kilograms.
Name of objects Weight in grams (g) Weight in kilogram (kg)
1. Bottle of water
2. Pencil
3. Eraser
4. Bag of sugar
5. Jug
6. Ruler
7. Stone
8. Bottle of Fanta
.
182
Name of objects Weight in grams (g) Weight in kilogram (kg)
9. Toothbrush
10. Orange
11. Rock
12. Scissors
13. 5 tins of Milo
14. A bundle of nails
15. 2 notebooks
16. A baby boy
Grams and kilograms
1000 grams (g) = 1 kilogram (kg)
short form short form
We can convert weights in grams to kilograms and weights in kilograms to grams
Examples
2 kg = 1000 g + 1000 g = 2000 g
1/2kg = 1000 g ÷ 2 g = 500 g
2000 g = 2000 g ÷ 1000 g = 2 kg

Exercise 2
A. Answer these.
1. How many kilograms are there in these:
a) 3000 g = b) 2500 g = c) 4000 g =
2. What must I add to 700 g to make 1 kg?
3. How many grams are there in these:
a) 1/2kg = b) 1/4kg = c) 3/4kg =
4. Which is greater?
a) 2000 g or 11/2kg b) 1500 g or 1 kg c) 3500 g or 3 kg
1. Copy and complete the following. Use symbols > or <.
a) 200 g[] 1/4kg b) 2/5kg[] 300 g c) 100 g[] 1/5kg d) 1 kg[] 700 g
e) 900 g[] 3/4kg f) 400 g[] 1/2kg g) 3/5kg[] 1/2kg h) 3/4kg[] 1/2kg
i) 800 g []3/4kg j) 2/5kg[] 1/4kg
2. Copy and complete the following. Use the number line to help you.
a) 1/2kg =[] g b) 3/4kg =[] g c) 1/5kg =[] g d) 1/4kg =[] g e) 2/5kg =[] g f) 1/10 kg =[] g g) 3/5kg =[] g h) 4/5kg =[] g
3. Copy and complete the following. The first one is done for you.
a) 11/2kg =[] 1 kg +[] 12kg
= 1 kg + 500 g
= 1 kg 500 g
c) 31/4kg =[] kg +[] g
=[] kg +[] g
e) 1/15kg =[] 1 kg +[] kg
=[] kg[] g
b) 21/2kg =[] kg +[] 12kg=[] kg{} g
d) 23/5kg ={}| kg +{} g
={} kg {}g
f) 3 1/10 kg =() kg +() g
=() kg() g


Week 4
Topic: Capacity
The amount of liquid a container holds is called its capacity.
Liquids are things like: water, milk, kerosene, oil, petrol, juice, mineral water, etc.
The standard measure for liquids is the litre l and millilitre ml

Liquids in large containers are measured in litres.
Petrol and diesel are measured in litres.
Liquids in small containers are measured in millilitres.
Syrups, lotions and perfumes are measured in millilitres.
Exercise
1. Name five liquids measured in litres.
2. Name five liquids measured in millilitres.
Activity
Check the empty containers of liquids you used in your home. Bring in one that
has 1 litre written on it. Compare with your friends’ containers. Do they all have the
same shape?
Capacity of containers
Note
10 millilitres (ml) = 1 centilitre (cl)
10 centilitres (cl) = 1 decilitre (dl)
10 decilitres () = 1 litre (l)
1000 litres = 1 kilolitre (kl)
Exercise 1
A. How many litres or millilitres can each contain? Use a litre jug to measure.
Container Measurement in litres
1 Bucket
2 Cooking pot
3 Plastic basin
4. Big jerry can
5. Small jerry can
6. Jug
7. Mug
8. Water dispenser jar
9. Pure water sachet
10. Flask
DON’T STRESS, JUST LET PROFESSIONALS DO THE STRESS, CLICK HERE TO BUY THE COMPLETE LESSON NOTE FOR JUST 1500 NAIRA OR HIT THE IMAGE BELOW
OR HIT THE WHATSAPP BUTTON TO CONTACT US
ACCESS ALL LESSON NOTES
ACCESS ALL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
ACCESS ALL WORKSHEETS
ACCESS ALL JOBS ACCESS
ACCESS WAEC QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
